The Basics of Resistive Touch Screen Technology
| What Makes Touch Screen Technology Work | |
 | |
|
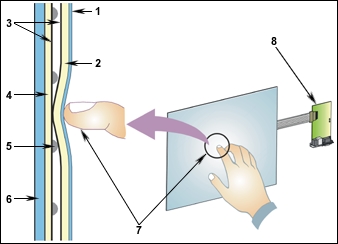
Resistive LCD touchscreen monitors have a flexible top layer and a rigid bottom layer separated by insulating dots, with the inside surface of each layer coated with a transparent metal oxide. Voltage applied to the layers produces a gradient across each layer. Pressing the flexible top sheet creates electrical contact between the resistive layers, essentially closing a switch in the circuit. The control electronics alternate voltage between this system of layers, the overlay, to get x then y touch coordinates. These x and y coordinates are then relayed to the computer's operating system through the touch screen controller connected to the overlay.
Resistive touchscreen technology possesses many advantage over other touchscreen technologies. Highly resistant and durable, resistive touch screens are less susceptible to contaminants than acoustic wave touchscreens and less sensitive to the effects of severe scratches than capacitive touchscreens are. In addition, resistive technology is more cost-effective for industrial applications than the more expensive Near Field Imaging (NFI) technology. Finally, resistive technology provides better touch sensitivity and resolution than infrared touch technology does.
Because of its versatility and cost-effectiveness, resistive technology is ideal for various markets and applications. These include food service and retail point-of-sale (POS), medical monitoring devices, industrial process control and instrumentation, portable and handheld products, and communication devices.
4-Wire, 5-Wire, and 8-Wire Resistive Touchscreens
Resistive touch technology exists in either 4-wire, 5-wire, or 8-wire form. 4-wire resistive technology is primarily restricted to small flatpanels (less than 10.4"). 5-wire touchscreens suffer from spacer dots and Newton rings problems. Neither account for high-level short-term variances between the resistive circuit layers nor have good axis linearity. Ultimately, 8-wire technology seeks to eliminate these deficiencies. 8-wire touchscreens, which are available in a variety of sizes, are less susceptible to Spacer Dots and Newton Rings. They have ligther spacer dots and substantially less problems with Newton rings.
No comments:
Post a Comment